Overview
Pipelines, Tasks, Transformations & Tables
- Pipeline: Is a set of Tasks. Executed by an orchestrator (e.g Apache Airflow/Oozie etc.)
- Task: An actual computation job that is being executed. for example A spark Job or a DBT project. A Task is comprised from a set of Transformations (TFs)
- Transformation: A single logical action such as an SQL query, a Spark Action or a DBT Model.
RF
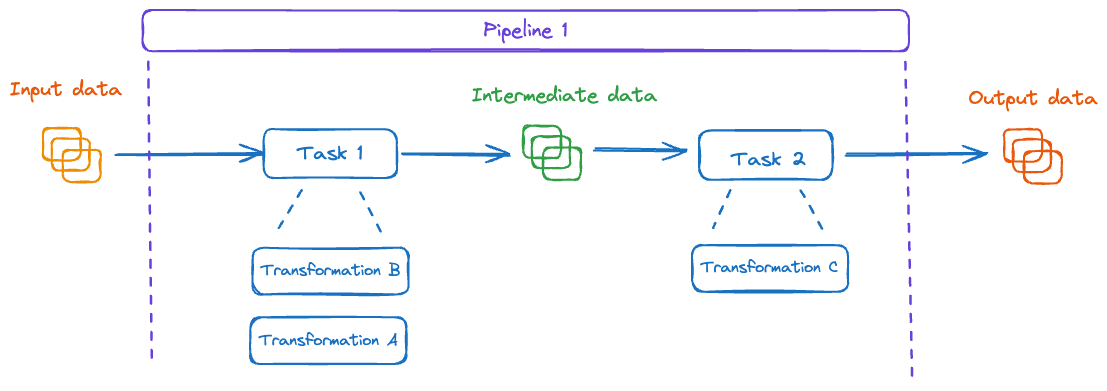
Definity agents are running as part of the Tasks execution and can observe all transformations and their Input/Output datasets. This is how Definity builds the task-dataset lineage and can also obtain column level lineage.
Point-In-Time (PIT) & Run Time
- Run Time Pipeline are executed every defined time period (for example every day @ 12:00) each specific start time is the Pipeline/Task/.
- Point In Time (PIT) Each such execution also has a logical time indicating the input data consumed. This is the PIT or logical date. A user can run the logical date 01/01/2020-22:00 with Run Time of 08/01/2024-14:00 and then again with Run Time of 09/01/2024-17:00
Metrics
Metrics are the basic building blocks of the monitoring in Definity. A metric is a numeric value that was measured on a specific asset (table/column or pipeline/task/transformation) in a specific execution (Run Time).
For example:
Pipeline: A / Task: B / PIT: 07-25-23 / Run Time: 07-25-26 / Table: T1
Metric type: volume count - Value: 1177500
Metric types
Metrics are split into five main analytical pillars of data observability:
- Time - metrics that measure the time dimension of the pipeline's data and execution. E.g., Freshness, Duration.
- Structure - metrics that measure the data structure consumed and generated by the pipeline. E.g., Schema (size, types, order).
- Content - metrics that measure the data values distribution and behavior. E.g., Uniqueness, Null, Value Distribution, Binning.
- Volume - metrics that measure the data volume. E.g., Total Row Count, Read Count, Write Count, Partitions, Files, Bytes.
- Behavior - metrics that measure changes in the data pipeline itself, the code, and the environment setup.
Metric profiles
- Metadata metrics - metrics that can be extracted for "free", with no additional query resource overhead. These metrics are calculated by the data platform (e.g., Spark, DBT, DWH).
- One-pass metrics - metrics that can be extracted with low (limited) additional query resource overhead, requiring only a single pass on the data.
- Advanced metrics - metrics that require more advanced data analysis and might require data shuffle or multiple scans.
Tests
A test is defined as the valid range of values for a specific metric.
If in a new execution of the pipeline the metric will have a value outside this range, the test will fail and an alert will be generated.
definity Test Engine begins to generate automated tests for a specific metric (for a specific pipeline) after a baseline for the metric was established.
- I.e., tests are only created after min ~4-5 pipeline executions are completed successfully with the specific metric.
- If a new metric is opted-in, ~4-5 successful pipeline executions are also required (to establish a baseline), before tests will be generated for it.
Test action definition:
| Name | Action | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Alert | Raise an alert | Currently alerts are internal in Definity. Email/Slack integration will be added |
| Pass | Ignore test failure | Used for temporary muting tests |
| Break | Stop pipeline execution | Currently not supported |